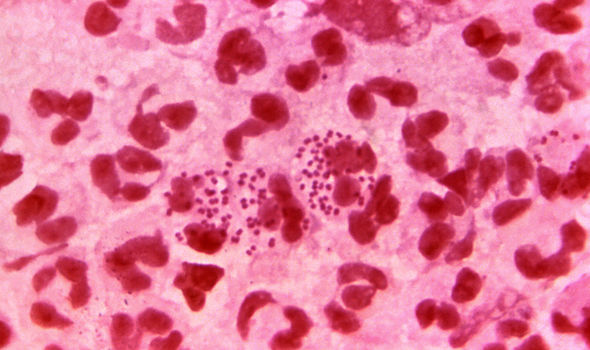
An Austrian man has reportedly contracted “super gonorrhoea”, after meeting with a sex worker in Cambodia.
Super gonorrhea, also referred to as super-resistant gonorrhea, is a sexually transmitted disease (STD) that is usually resistant to medical treatment.
According to a research paper published in Eurosurveillance, the man, who is in his 50s, had reported painful urination in April 2022 — days after he had unprotected sex with the female sex worker.
“In April 2022, a heterosexual male patient in his 50s consulted a urology department in Austria because of painful urination and urethral discharge. Five days before onset of symptoms, he had condomless heterosexual contact with a female commercial sex worker in Cambodia, who could not be traced,” the paper reads.
Advertisement
“Based on sexual history, a urethral swab was taken, and N. gonorrhoeae culture (AT159 strain) verified the gonorrhoea diagnosis.
“The patient was treated with ceftriaxone (1 g intramuscularly) plus azithromycin (1.5 g single oral dose), according to European recommendations but using a slightly adapted azithromycin dosing (1.5 g instead of 2 g).
“Approximately 2 weeks later at a follow-up visit, symptoms had resolved. Test of cure using culture of urethral, rectal and pharyngeal samples was negative, however, a PCR test (Allinity, Abbott, Chicago, Illinois, United States (US)) from the urethral swab culture sample was N. gonorrhoeae-positive.
Advertisement
“Because no post-treatment gonococcal isolates were available, the case was considered as a possible treatment failure.”
Describing the strain as a “major global public threat”, the scientists said such class of gonorrhea is usually resistant to several forms of treatment.
“In the absence of a gonococcal vaccine, early and effective diagnosis and antimicrobial treatment of gonorrhoea are essential. However, N. gonorrhoeae has developed resistance to all classes of antimicrobials since introduction of antimicrobial treatment in the 1930s,” the report reads.
“XDR N. gonorrhoeae strains, including those with resistance to all available treatment options, are a major global public health concern. They pose a risk of treatment failure and serious complications/sequelae on the individual level but also compromise the management and control of gonorrhoea on the public health level.”
Advertisement
The scientists, however, cited some recommendations for managing the threat of the strain gaining momentum, including raising awareness on preventive measures such as the use of condoms, and appropriate diagnosis where necessary.
“Ultimately, novel antimicrobials for effective treatment of gonorrhoea and/or a sufficiently effective gonococcal vaccine will be crucial,” they added.
Add a comment